New Delhi13 minutes ago
- Copy link

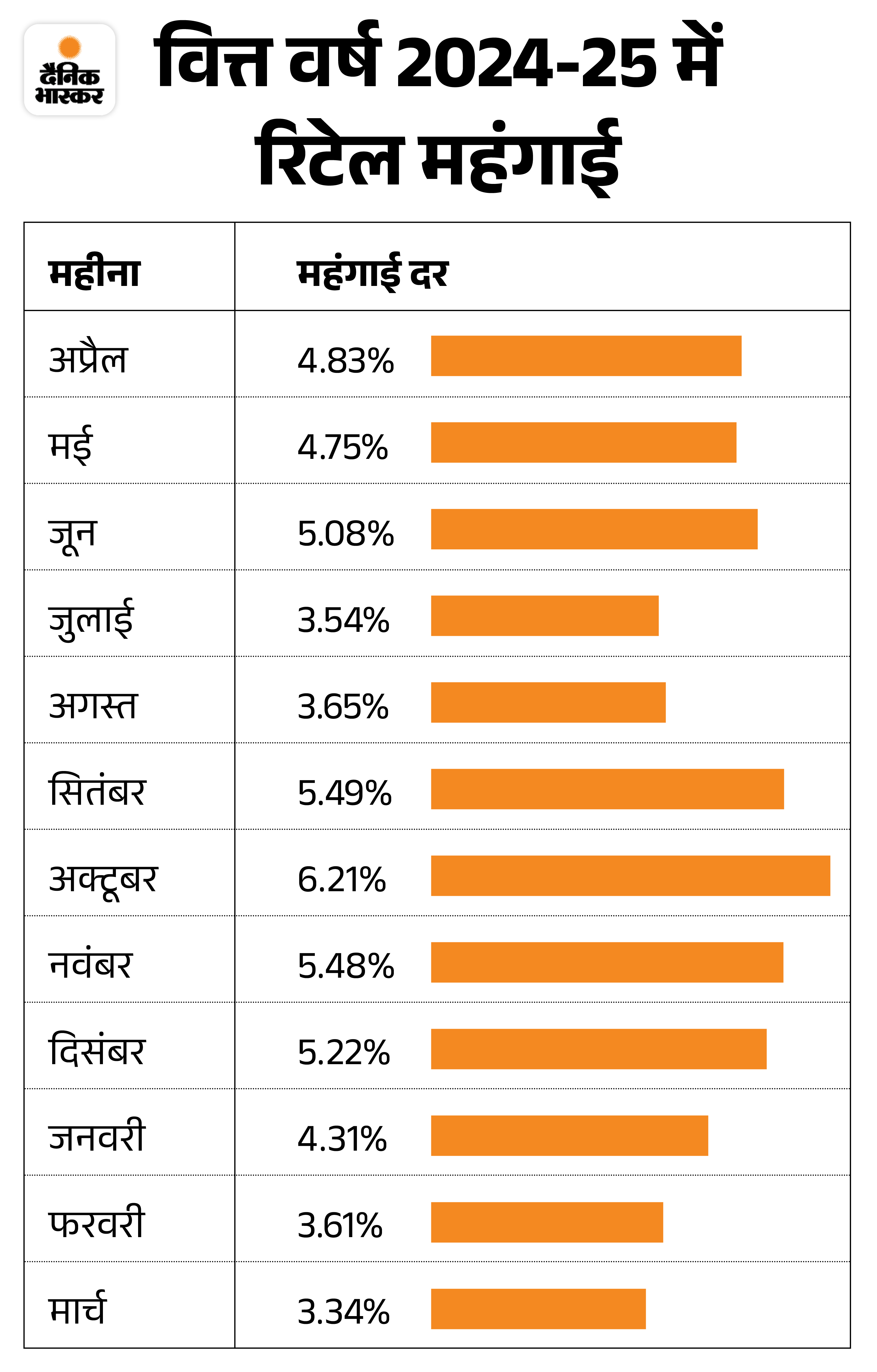
India’s retail inflation is expected to be less than 2.50% in June. Earlier in May, it came to 2.82%. This was a 6 -year low. Earlier in March 2019 it was 2.86%. Retail inflation was at 3.16% in April.
Retail inflation may decrease further due to continuous softness in the prices of food items. Today i.e. on July 14, retail inflation figures will be released. Retail inflation is below 4% of the RBI target from February.
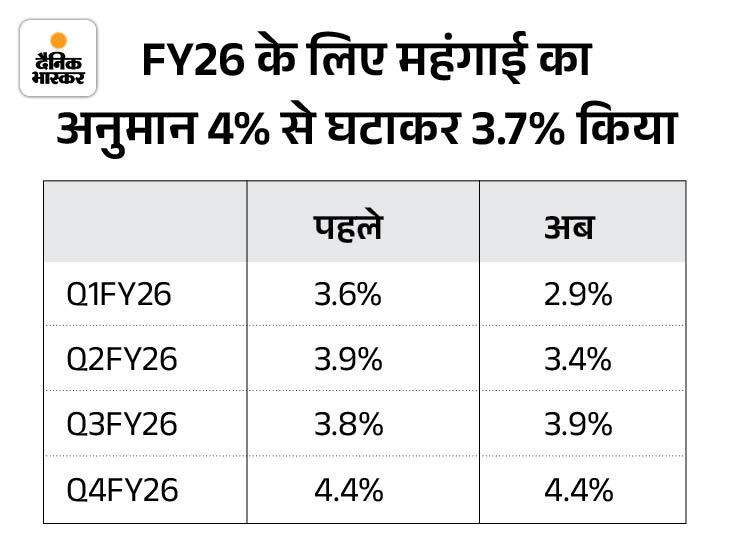
RBI reduced inflation estimate Earlier, in the meeting of the RBI Monkey Policy Committee held from 4 to 6 June, the inflation for FY 2025-26 was reduced from 4% to 3.7% for the financial year 2025-26. RBI reduced its inflation estimate from 3.6% to 2.9% for the April-June quarter.
How does inflation grow? Increased inflation and the event depends on the demand and supply of the product. If people have more money, then they will buy more things. Buying more things will increase the demand for things and if there is no supply according to the demand, the price of these things will increase.
In this way, the market is in the grip of inflation. Simply put, excessive money in the market or shortage of things causes inflation. On the other hand, if the demand will be reduced and more supply will be reduced.
CPI determines inflation As a customer, you and we buy goods from the retail market. Consumer Price Index i.e. CPI does the work of showing changes in the prices associated with it. The CPI measures the same for goods and services that we pay for goods and services.
Crude oil, commodity prices, manufactured costs, also have many other things which have an important role in fixing retail inflation. There are about 300 items, based on the prices, the rate of retail inflation is fixed.



