New Delhi2 minutes ago
- Copy link

The performance of Indian companies has been interesting for the last 10 years. During this time, every year his profit growth increased more than one and a half times. This difference increased from 2020.
The annual increase in their profits reached around 26% twice as compared to sales. That is, the Indian Corporate Sector has performed strongly since the Kovid epidemic.
The biggest reason for this was that their profit margin increased to 12% between FY 2024-25, which was less than 8% in 2014-15.
Pure profits up on average 16% on average every year
In 10 years by 31 March 2025, the sale of Indian companies increased annually from 9.7% compounded rate (CAGR). Meanwhile, their net profit increased by an average of 16% every year.
The sale of companies between the financial year 2019-20 and 2024-25 increased an average of 12.7% on an average every year, but their net profit increased an average of 25.7% year.
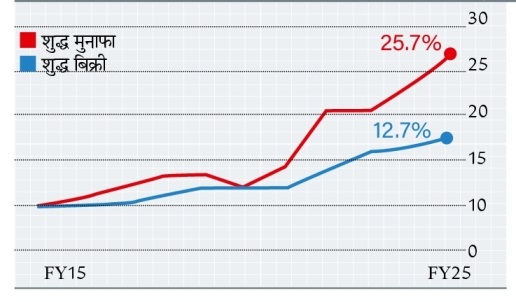
Pre-tax margin of companies increased by 3% in 10 years
In 10 years, the net profit margin of listed companies increased from 5% to 8.8%. But these do not include banking, financial services, insurance, oil-gas and IT companies. This means that companies of these sectors have performed better. On inclusion of these, the average margin of the Indian corporate sector reaches 12%.
Profit margin reached peak in 25 years
Dhananjay Sinha, a co-head (research and equity strategy) of Systematic Institutional Equity, said, “Our figures suggest that the profit margin has reached the highest level (peak) in most sectors during the last 25 years.”
The closure of small companies increased the strength of large companies; Manmarji prices increased, this increased profits
According to Sinha, the reign of large companies in the market increased as they acquired many small companies. At the same time, some small companies closed themselves.
Due to this, big companies were able to increase the prices of products and services according to need and will. There were three major reasons for this …
- In the GST framework, small-scale small companies could not mold themselves.
- The IBC i.e. Bankrupt Code made it easier to acquire struggling companies.
- Due to the strict lockout in Kovid, it became difficult for a lot of small companies with low capital to stay in the market.
,
Read this news too …
1. Retail inflation came to a 6.5-year low: It was 2.10% in June, inflation declined due to cheap food items

Retail inflation in the month of June has come down to 2.10%. This is a low of 77 months. Earlier in January 2019 it was 2.05%. At the same time, it was 2.82% in May 2025 and retail inflation in April 2025 at 3.16%.
Retail inflation has decreased due to continuous softening in the prices of food items. Today i.e. on July 14, retail inflation figures have been released. Retail inflation is below 4% of the RBI target from February.
Click here to read the full news …
2. Wholesale inflation at 20 months low: It was 0.13% in June, food prices decreased

The wholesale inflation in the month of June has come down to minus 0.13%. This is its 20 -month low. Earlier in October 2023 it was minus 0.56%. It was 0.39% in May 2025 and 0.85% in April 2025. Inflation has reduced due to the decrease in the prices of daily needs and the prices of food and drink.
Click here to read the full news …